
The SECURE 2.0 Act makes major changes to the required minimum distribution rules.
When you purchase through links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission. Here’s how it works.

There are some new rules for required minimum distributions (RMDs) from retirement savings accounts (e.g., traditional IRAs and 401(k) plans). The SECURE 2.0 Act of 2022 makes significant changes to the way people save for and are taxed in retirement. RMDs are one of the major areas of focus in the law.
It wasn't all that long ago that the retirement-savings landscape was shaken up. Among other things, the original SECURE Act, enacted five years ago extended the age at which you must start taking RMDs from 70½ to 72. But that wasn't enough help for retirees in the eyes of many lawmakers. So, Congress began planning additional legislation to help more people save for retirement and hold on to their money longer. Those efforts resulted in the SECURE 2.0 Act.
Getting up to speed on the new changes is important for retirees, or those approaching retirement, who are worried about required minimum distributions (RMDs).
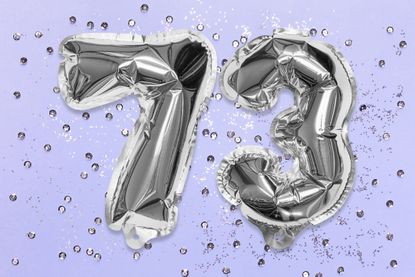
Before the SECURE 2.0 Act you had to start taking RMDs from 401(k) accounts, traditional IRAs, and similar retirement savings accounts (other than Roth IRAs) in the year you turned 72 (although you had until April 1 of the following year to take your first RMD). However, the SECURE 2.0 Act eventually pushes the age for starting RMDs to 75 after moving it to 73 as of 2023.
There is a two-step process under the SECURE 2.0 Act for increasing in the age when RMDs become necessary. Step 1: Beginning in 2023, the age to start taking RMDs jumped from 72 to 73. Step 2: Beginning in 2033, it creeps up again to 75.

The SECURE 2.0 Act reduces the penalty for failing to take an RMD to 25% in all cases. In addition, the penalty drops down to 10% if you take the necessary RMD by the end of the second year following the year it was due.
For some, the SECURE 2.0 Act will also delay the start of the statute of limitations for assessing the penalty. For people who are not required to file an income tax return for the tax year in question, the three-year limitations period starts on the date that an income tax return would have been due (excluding any extensions), instead of the date a tax return for the year is actually filed, which can be later than the normal due date. By starting the clock sooner, some people might avoid the penalty if the IRS is slow in assessing it.
Note: Keep in mind that the IRS has waived penalties for failing to take RMDs for certain inheritied IRAs. For more information, see IRS Delays IRA RMD Rules.

There are no RMDs for Roth IRAs. However, RMDs are currently required for Roth 401(k) accounts. You can get around the Roth 401(k) RMD rules by rolling over the money into a Roth IRA. But watch out for the Roth IRA five-year rule – if you are not careful, you may have to wait five years to pull your money out of the Roth IRA.
The SECURE 2.0 Act eliminates the need to roll over funds from a Roth 401(k) to a Roth IRA. Instead, as with Roth IRAs, Roth 401(k) accounts won't be subject to the RMD rules before the account holder dies. (Post-death minimum distribution rules, which also apply to Roth IRAs, still apply.)
This change generally kicked in starting this year, 2024. However, an exception applies to RMDs required before 2024 but not required to be paid until January 1, 2024, or later.

The SECURE 2.0 Act addresses a few issues related to the use of annuities with retirement savings accounts.
For instance, if a retirement account includes an annuity, the account was split under prior law between the part holding the annuity and the part that doesn't for purposes of applying the RMD rules. This could result in higher RMDs.
SECURE 2.0 allows you to combine distributions from both parts when calculating your annual RMD amount.
In addition, to help make annuities a more attractive component of retirement plans, SECURE 2.0 allows the following payments if certain requirements are satisfied:
Finally, SECURE 2.0 boosts the use of qualifying longevity annuity contracts (QLACs). Generally, with a QLAC, you can invest up to $200,000 (2024 amount) or 25% of a retirement account, whichever is less, and shield those funds from RMDs.
SECURE 2.0 repeals the 25% limit and bumps the dollar amount up to $200,000 (adjusted for inflation each year). It also clarifies that (1) survivor benefits can be paid following a divorce, and (2) an employee has 90 days from the purchase date to rescind a QLAC.

Special rules exist for determining when a surviving spouse must start taking RMDs from an inherited retirement account.
One of those rules states that, if an account holder dies before RMDs are required and their surviving spouse is the beneficiary (and doesn't change that status), RMDs from the inherited account aren't required until the year in which the deceased account holder would have reached age 72.
SECURE 2.0 tweaks that rule by also allowing the surviving spouse to be treated as the deceased account owner for RMD purposes starting in 2024. In some cases, this will allow the surviving spouse to delay taking RMDs from the inherited account, e.g., if the surviving spouse is younger than the deceased spouse.
The surviving spouse will have to elect this treatment according to procedures the IRS will have to establish, and the election will be irrevocable. The surviving spouse will also have to notify the account administrator.

Money donated to charity through a qualified charitable distribution (QCD) counts towards your RMD. So, for charitable-minded older adults, QCDs are a great way to reduce the amount of money you otherwise have to withdraw from an IRA. However, QCDs were previously capped at $100,000 per year.
SECURE 2.0 allows the QCD limit to be adjusted annually for inflation (rounded to the nearest $1,000). The adjustments began as of 2024. So, the limit for 2024 is $105,000.
In addition, as of 2023, a one-time QCD of up to $50,000 to charities is allowed through certain charitable remainder annuity trusts, charitable remainder unitrusts, or charitable gift annuities.